Janus hydrogels, with their distinctive uneven constructions, show incomparable benefits over conventional supplies in mucosal moist tissue defect restore. Mucosal tissues within the physique (such because the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and reproductive tract) exhibit advanced physiological traits excessive water content material (> 90%), dynamic enzymatic surroundings, pH gradient variations, and mucus layer barriersimposing stringent necessities on restore materials efficiency. Moist environments trigger fast hydrogel swelling: pure polymers like collagen present swelling ratios exceeding 10 occasions the preliminary quantity because of robust hydrophilic group-water interactions, accompanied by mechanical energy discount [89]. Artificial hydrogels might endure quantity section transitions on the mucosal physiological temperature (37℃), compromising structural integrity. Such swelling not solely accelerates hydrolysis but in addition shortens bodily crosslinked hydrogel community disintegration time by over 50%. Janus uneven structural designs considerably improve the anti-swelling efficiency and mechanical stability of supplies. Particularly, the hydrophobic layers can successfully inhibit swelling [89]and the dense porous constructions constructed by solvent change can enormously scale back the swelling ratio to six.4% [90]. These design components work collectively to result in such notable enhancements.
Considerable enzymatic actions in mucosal tissues (e.g., proteases, hyaluronidases) additional affect materials degradation conduct: trypsin hydrolyzes peptide bonds in gelatin-based hydrogels, inflicting 40% weight reduction inside 30 min; hyaluronidase exercise will increase 3–5 fold in infected mucosa, considerably shortening materials lifespan. Moreover, enzymatic degradation merchandise might set off immune responses (e.g., chitosan oligosaccharides activating Toll-like Receptor 4(TLR4) receptors to stimulate pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion). Introducing nanoclay-limited enzymatic know-how (e.g., GPC hydrogels [90]) delays degradation whereas enabling managed drug launch, avoiding TLR4 receptor activation by degradation merchandise like chitosan oligosaccharides.
pH fluctuations in mucosal tissues (e.g., gastric pH 1–3 vs. intestinal pH 6–8) regulate degradation and drug launch by altering materials chemical microenvironments: poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels exhibit 50% diminished swelling underneath acidic situations because of carboxyl protonation, whereas ionic dissociation accelerates swelling in alkaline environments. Janus hydrogels can combine pH-responsive parts (e.g., rhein/graphene oxide composites [91]) with zwitterionic surfaces (poly (sulfobetaine)) to realize synergistic results of acidic surroundings drug launch and impartial area mucus anti-adhesion.
Mucus layer limitations (100–500 μm–thick, containing mucins andglycosaminoglycans) affect materials efficiency by bodily and chemical mechanisms: their excessive viscosity (1–100 mPa·s) and nanoscale community constructions (10–100 nm pore dimension) scale back drug diffusion coefficients to 1/a centesimal of these in water, whereas negatively charged glycosaminoglycans type bodily limitations with positively charged chitosan. Steady mucus layer renewal (turnover time 1–6 h) leads to unmodified hydrogel half-lives < 2 h, whereas PEGylated floor modifications [92] (e.g., conductive polypyrrole zwitterionic layers) prolong this to over 6 h, overcoming dynamic mucus renewal limitations. Moreover, mucus adsorption might set off protein biofilm formation, impeding cell adhesion and tissue regeneration, and releasing pro-inflammatory substances like histamine. These advanced environmental components collectively current multi-dimensional challenges for Janus hydrogel design, requiring modern materials structural designs and practical integrations to exactly handle a number of mucosal restore necessities. These embody the necessity to rapidly restore mucosal defects, stop exterior aggression, preserve the moist surroundings, promote the proliferation of epithelial cells, restore the perform of mucous membranes, keep away from postoperative adhesion of tissues and scale back problems, present a steady surroundings for tissue progress, and forestall the invasion of non-target cells, permitting monitoring of the wound. Furthermore, restore supplies ought to be capable to exactly ship medicine to the designated web site and obtain the focused loading and launch of the drug throughout minimally invasive surgical procedure. Standard restore strategies typically battle to fulfill these advanced wants, and Janus hydrogels provide modern options in mucosal defect restore, anti-adhesion, site-preserving performance, stimulus monitoring, and exact drug supply.
Defect restore perform
Janus hydrogels present an instantaneous bodily barrier for mucosal defects by mimicking the traits of pure mucosal tissues, accelerating the migration and proliferation of epithelial cells, and selling the fast restore of the faulty space. Mucosal tissue defect restore could be utilized to the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, and different digestive tract mucous membranes. Conventional adhesive hydrogel adhesion could cause critical adhesion between broken and regular tissues. Janus hydrogels present a bodily barrier to advertise wound therapeutic and obtain tissue adhesion underneath moist situations by the properties of bioadhesives, stopping and minimizing issues comparable to mutual adhesion.
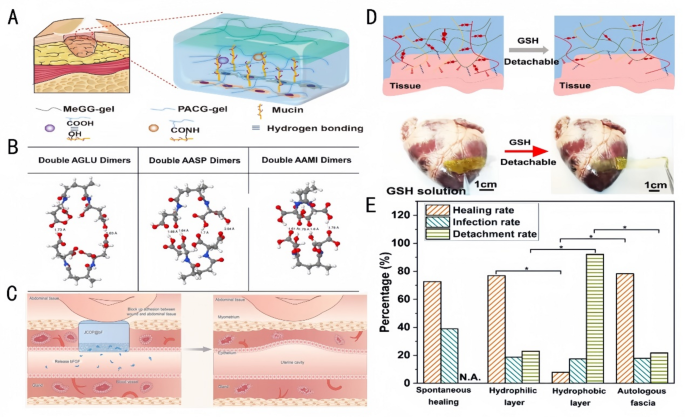
Oral ulcer (OU) is a typical oral mucosal illness characterised by persistent defects within the mucosa or the disruption of epithelial integrity, thereby affecting the protecting perform of the mucosa [93, 94]. Supplies for the remedy of OU typically face issues comparable to poor adhesion, simple washing away by meals or saliva, brief adhesion time, delamination, and fast degradation [95]. Xing et al. [96] fabricated two totally different practical layers of the Janus patch. One facet was a clean layer consisting of double-bonded modified junction coolant gel (Fig. 8A), which reduces non-specific adhesion and thus prevents secondary harm to the encircling wholesome oral mucosal tissue. On the opposite facet was a Methyl Glycidyl Ether (MeGG) layer, which inhibits TGF-β1 binding to its receptor (IC50 = 0.8 µM), thereby decreasing α-SMA expression by 40% and suppressing fibroblast adhesion. This helps stop extreme fibrosis throughout oral tissue therapeutic, sustaining the integrity and performance of oral mucosa. The Janus patch demonstrates speedy moist adhesion with extended adherence time, whereas selling keratinocyte migration (migration charge of 0.15 mm/h) by integrin α6β4-mediated signaling pathways. It additionally upregulates K14 expression (mRNA upregulation by 2.5-fold), accelerates fibroblast progress, and promotes capillary/granulation tissue formation. Withstanding oral actions comparable to mastication and occlusion, the patch achieves superior therapeutic outcomes. An et al. [90] reported the preparation of a Janus Gelatin-Polydopamine-nanoclay (GPC) hydrogel. This hydrogel achieved excessive interfacial adhesion energy and robust toughness underneath wetting situations by the binding of its catechol moiety to particular practical teams (e.g., -NH2, -SH, -OH, and -COOH) on the tissue floor. As well as, the hydrogel had excessive mobile affinity, which facilitated cell adhesion and proliferation, thus selling the therapeutic of OUs. Liu et al. [97] developed a Janus hydrogel patch with wonderful moist adhesion and self-debonding properties. The patch consisted of a troublesome layer, composed of PEGDA and PVA, to supply mechanical energy and power dissipation, and an adhesion layer combining N-[Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]acrylamide (THMA) and CS to realize robust adhesion to moist tissues by using the excessive density of hydroxyl hydrogen bonding in THMA (Bonding energy: 8 kPa) and the topological adhesion of CS. The hydrogel promotes fibroblast proliferation (Brdu-positive charge elevated by 60%) by activating the FAK/PI3K pathway, whereas concurrently inhibiting MMP-9 exercise (exercise diminished by 55%) to cut back ECM degradation and facilitate mucosal restore. As well as, the self-unbonding property of the hydrogel helped keep away from secondary harm to the repaired tissue. Chen et al. [98] additionally developed a thermosensitive Janus dressing based mostly on poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PEG-PTMC) copolymers for oral ulcer remedy, attaining exact drug supply and accelerated mucosal restore by in situ section transition. The bilayer construction kinds at oral mucosal temperature (37℃): an internal drug-loaded precipitated layer with 80 kPa adhesion energy and an outer moisture-retaining gel layer sustaining 95% hydration. Hydrophobic dexamethasone (DEX) achieves 50% cumulative launch over 72 h, whereas hydrophilic dexamethasone phosphate (DXM-P) offers 80% burst launch inside 3 h, tailoring remedy for acute and persistent phases. In vivo rat fashions demonstrated 81% ulcer closure by day 7 (vs. 65% for Tegaderm), with 34.1 μm epithelial thickness (near native mucosa) and 89% collagen deposition with organized fibrils. Amorphous PTMC section ensures viscoelastic adhesion to moist mucosal surfaces, whereas the Janus construction offers steady hydration and 99.8% bacterial invasion blocking. Histological evaluation revealed 3 occasions the quantity of VEGF expression selling angiogenesis and restored nerve fibers (NF200+), indicating scarless therapeutic. All research addressed the challenges of inadequate adhesion and fast drug loss in conventional oral ulcer dressings by materials design. Amongst them, Chen et al.’s thermosensitive dressing demonstrated superior therapeutic outcomes because of its exact drug supply and biomechanical compatibility, attaining scarless therapeutic with 81% ulcer closure in 7 days and restoring mucosal integrity.
Hydrogel efficiency in adhesion and tissue restore. A: Schematic overview of the interactions between ACG and mucin [96]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier. B: The optimized conformation for double AGLU dimers, double AASP dimers, and double AAMI dimers; white, grey, blue, and crimson White, grey, blue, and crimson balls symbolize H, C, N, and O atoms, respectively. The dashed strains denote hydrogen bonds [100]. Copyright 2022, Elsevier. C: Utility of JCOP@bF in a rat mannequin of extreme uterine damage, detailing its position in stopping adhesions and selling JCOP@bF has a bodily barrier to dam adhesions and has a slow-release bFGF issue to manage the uterine. JCOP@bF can successfully promote the restoration of the uterus and help dwell delivery in rats [101]. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH GmbH. D: Schematic diagram of dissociation of a Cationized Polymethylmethacrylate(CPAMC) hydrogel triggered by GSH [91]. Copyright 2023, Nature Communication. E: Comparability of the therapeutic, the an infection, and the detachment charges of guinea pigs with TM perforations after spontaneous therapeutic with the hydrophilic and the hydrophobic surfaces of JMs-22 and with the autologous fascia [104]. Copyright 2022, The Royal Society of Chemistry
For visceral tissue mucosal defect purposes, comparable to gastric mucosal tissue defect restore, Liang et al. [99] achieved instantaneous moist adhesion and anti-swelling properties as an entire by combining Polyacrylic Acid (PAA), gelatin (GT), and catechol (HBPC)-modified hyperbranched polymers, which might preserve good cohesion and adhesion as gastric perforation restore supplies. Yu et al. [100] achieved good cohesion and adhesion with a gastric perforation restore materials by way of the free radical polymerization of N-acryloylaspartic acid (AASP) (Fig. 8B). The synergistic impact of interfacial interactions and cohesive power between the polymer molecules and the adherent surfaces was achieved by finely tuning the spatial web site resistance of the polymer molecules, demonstrating adhesion strengths of as much as 120 kPa. Janus hydrogel patches based mostly on this precept obtain the properties of being adhesive but proof against undesirable adhesion by adhesive and non-adhesive floor bonding for wound therapeutic and practical reconstruction and provide nice potential as bioadhesives for emergency rescue and tissue/organ restore. Restore of uterine defects by the implantation of Janus hydrogel patches for tension-free therapeutic can deal with uterine anomalies and infertility. Kang et al. [101] achieved superior protection of uterine defects and considerably improved dwell delivery charges utilizing the novel Janus Collagen Patch (JCOP) (Fig. 8C). With its uniform composition resembling homologous tissues, JCOP carefully matches the pure uterus in construction, micromorphology and performance. The tough floor and free extracellular matrix-like porosity of JCOP promote fibroblast adhesion and endometrial tissue regeneration, whereas its clean floor reduces fibroblast adhesion. The Janus construction design not solely promotes the restore of broken uteruses, restoring endometrial thickness to 89.7% of regular ranges and growing vascular density by 2.3-fold, but in addition restores endometrial embryo receptivity, holding important potential for purposes in treating infertility brought on by uterine damage. A current research highlights the potential of polysaccharide-based hydrogels in uterine mucosal restore. Particularly, a bilayered alginate-hyaluronic acid (Alg-HA) hydrogel fabricated by way of 3D extrusion-based bioprinting demonstrated enhanced endometrial regeneration in a rat mannequin of uterine damage. This assemble supported endometrial epithelial cell (EEC) monolayer formation and stromal cell (ESC) proliferation, restoring endometrial thickness and enhancing being pregnant outcomes. The hydrogel’s biodegradability and biocompatibility enabled managed launch of bioactive components, fostering neovascularization and decreasing fibrosis. Moreover, a 3D-printed bilayer alginate-hyaluronic acid (Alg-HA) hydrogel not too long ago developed for uterine mucosal restore combines biocompatibility and managed degradation to realize sequential launch of VEGF and primary fibroblast progress issue (bFGF) [102]. The hydrogel’s micro-nanoporous structure promotes migration and colonization of endometrial epithelial cells (EECs) and stromal cells (ESCs), whereas concurrently inhibiting fibrosis-related proteins by way of the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. These mechanisms restore injured endometrial thickness to 89.7% of regular ranges and improve vascular density by 2.3-fold in comparison with untreated controls. These findings underscore the utility of polysaccharide-based hydrogels in addressing advanced mucosal defects, comparable to intrauterine adhesions, by combining structural help with regenerative cues.
Myocardial infarction (MI) is among the main causes of loss of life worldwide. Multifunctional hydrogel cardiac patches with Janus adhesion properties and uneven double-sided particular options can allow MI restore and forestall secondary trauma. For instance, He et al. [91] achieved non-invasive cardiac restore and tissue adhesion prevention by Janus hydrogels, which supplied mechanical help and electrical signaling within the area of MI (Fig. 8D), promoted cardiomyocyte maturation and functionalization, re-established electrical conductivity and blood provide within the infarcted space, and repaired myocardial damage.
The tympanic membrane performs an essential position within the human auditory system and is vulnerable to perforation underneath unfavorable situations, resulting in listening to loss and otitis media [103]. Janus hydrogels could be utilized to cowl tympanic membrane perforation because of their perform of unilateral cell progress. Zhang et al. [104] co-deposited a tannic acid (TA)/3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) coating on the floor of polypropylene microfiltration membrane, thus developing Janus membranes with uneven cell adhesion conduct (Fig. 8E). The hydrophilic facet additionally healed tympanic membrane perforations and restored broken listening to. The distinction in wettability between its two sides resulted in uneven cell adhesion properties, which prevented the restore materials from adhering to the auditory ossicles, thus decreasing listening to loss. Due to this fact, the development of Janus hydrogels that facilitates unilateral cell progress is essential for the research of latest supplies for tympanic membrane restore.
Based mostly on the above literature, the mucosal restore mechanism of Janus hydrogels could be additional supplemented as follows: Their bilayer construction promotes restore by synergistic results: (1) The hydrophobic layer inhibits enzymatic degradation (e.g., pepsin) to extend materials longevity; (2) The hydrophilic layer masses progress components (e.g., bFGF) for managed launch, accelerating epithelial cell migration; (3) The micro-nano porous construction mimics the extracellular matrix, offering a three-dimensional progress scaffold for cells. These mixed actions collectively promote mucosal restore. Due to this fact, Janus hydrogels present nice potential within the restore of assorted mucosal tissue defects, which may re-establish the protecting barrier to forestall the invasion of exterior dangerous components and assist restore the secretion and absorption capabilities of the mucosa, promote wound therapeutic, and scale back scar formation, successfully overcoming the constraints of conventional supplies. Nonetheless, a lot is unknown in regards to the particular physiological surroundings of various mucosal tissues and the variations in restore wants. Sooner or later, we will additional optimize the efficiency of Janus hydrogels based mostly on the traits of various mucosal tissues, such because the digestive fluid surroundings of the gastrointestinal tract and the cyclic physiological adjustments of the uterus, to enhance the impact of its restore. For instance, for gastrointestinal mucosal restore, Janus hydrogels could be designed with acid- and enzyme-resistant properties, and on the similar time, mixed with progress components that may promote the proliferation and differentiation of gastrointestinal mucosal cells to boost the restore impact. For uterine mucosal restore, Janus hydrogels could be developed to answer hormonal adjustments and promote the angiogenesis of the endometrium to raised meet the particular wants of uterine restore. Lengthy-term animal and scientific research are wanted to additional validate the protection and efficacy of Janus hydrogels in mucosal defect restore.
Anti-adhesion perform
Postoperative wounds are sometimes related to the exudation of blood and tissue fluids, leading to a moist tissue interface that’s detrimental to wound restore. Moist tissue surfaces and the mutual contact of various organs in a steady, dynamic, in vivo surroundings, particularly within the stomach and chest, predispose to moist tissue surfaces and organ adhesions. Janus hydrogels are efficient in decreasing postoperative adhesion problems by advantage of their adhesion and anti-adhesion properties due to their uneven construction—by facilitating tissue adhesion and on the similar time stopping undesirable tissue adhesions [105].
In a rabbit mannequin of gastric perforation, Cui et al. [106] demonstrated fast and robust tissue adhesion in a moist surroundings by a Janus hydrogel with each adhesive and anti-adhesive properties. Nonetheless, the opposite facet of the hydrogel confirmed non-adhesive properties as a result of the carboxyl teams had been utterly neutralized, thus decreasing adhesion to the tissue. Thus, this Janus hydrogel might successfully stop postoperative tissue adhesion and scale back secondary harm throughout surgical procedure. This hydrogel is predicted to interchange conventional surgical sutures, scale back postoperative problems, and promote simpler tissue restore [107]. p(AA-co)-crylate was developed by forming a base layer from a copolymer of acrylic acid (AA) and 2-aminoethyl methacrylate (AMA), known as p(AA-co-AMA). p(AA-co-AMA) is a brand new multifunctional Janus tissue adhesive that ensures quick adhesion to moist tissues, and on the similar time, offers wonderful anti-adhesion properties. The anti-adhesive properties are primarily supplied by a high layer of acrylic acid homopolymer (PAA) and a 2-aminoethyl methacrylate copolymer containing betaine sulfate (Zwitterionic Sulfobetaine/Aminoethyl Methacrylate Copolymer, p(AMA-co-SBMA)), known as AASB composition. The AASB successfully inhibits cell and tissue adhesion and reduces inflammatory responses, offering a brand new technique for sutureless wound remedy and exhibiting nice potential in blocking postoperative gastric mucosal tissue adhesion. Postoperative tissue adhesions between intestinal tissues and different organs can result in a collection of problems, comparable to long-term pelvic ache, intestinal obstruction, and infertility, and often require a second surgical procedure to alleviate the undesirable tissue adhesions. Furthermore, present anti-adhesion biomaterials comparable to Interceed, Seprafilm, and anti-adhesion fluids lack tissue adhesion on the tissue-contacting facet and fail to securely adhere to the tissue. Li et al. [10] successfully regulated the adhesion on the highest facet by complexing the GA-PAA facet with PVA to type a dense and porous floor. This formation results in a discount in fibrinogen adsorption, with the adsorption quantity dropping from 200 µg/cm² to 30 µg/cm². On the similar time, it inhibits fibroblast migration, inflicting a 70% lower within the migration distance. Because of this, it successfully modulates the adhesion on the highest floor and prevents postoperative tissue adhesion. Moreover, the abundance of carboxyl teams promotes tissue adhesion by hydrogen bonding, offering preferrred adhesion for intestinal restore.
Based mostly on the widespread postoperative adhesion issues after open stomach and different surgical procedures, Liu et al. [108] constructed a superhydrophilic amphiphilic polymer based mostly on a bionic microstructure. Its single-component Janus amphiphilic hydrogel patch might improve the adhesive energy by the bionic microstructure of small hexagonal surfaces separated by interconnecting grooves, and on the similar time, act as a bodily barrier with superior anti-adhesion results. Liang et al. [109] utilized the porous construction and clean backside floor of a porous polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel (JPVA hydrogel) to cut back fibroblast adhesion, whereas the tough high floor improved fibroblast adhesion and tissue progress. This construction additionally had anti-deformation and anti-adhesion properties, which will probably be helpful in open stomach surgical procedures to cut back undesirable adhesion whereas enhancing adhesion to tissues. Han et al. [110]developed a Janus polypropylene mesh (PPM) by way of surface-initiated photopolymerization to handle postoperative adhesion (PA) in hernioplasty. The mesh options uneven capabilities: one facet coated with zwitterionic polymer brushes (PS) to dam 99% protein adhesion and cell attachment, whereas the alternative facet immobilizes hole polydopamine nanoparticles (HAP) loaded with antimicrobial peptide (AMP) and platelet lysates (PLs). The PHAP layer achieves ROS-scavenging effectivity of 85%, reduces IL-6 expression by 70%, and promotes fibroblast migration (0.15 mm/h) by way of integrin α6β4 signaling. In vivo rat fashions confirmed 100% bacterial clearance (S. aureus/E. coli) and full adhesion prevention (adhesion rating 0/14 days), surpassing business meshes (rating 9.7). Histological evaluation revealed 89% collagen deposition with organized fibrils and thrice the quantity of CD31 + angiogenesis, indicating scarless therapeutic. Li et al. [111] developed an anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic Janus hydrogel (PAA-Cos@ Ligustrazine (Ligu) by a composite design of cationic chitosan oligosaccharides (COS) and anionic PAA, attaining uneven adhesion properties on each side. The adhesive facet kinds covalent bonds with tissue surfaces by way of carboxyl teams, whereas the alternative facet inhibits protein adsorption by zwitterionic constructions, successfully stopping peritoneal adhesions throughout wound restore. PAA-Cos@Ligu promotes M2 macrophage polarization and suppresses the TGF-β/Smad 2/3 signaling pathway, decreasing collagen deposition and myofibroblast differentiation. In a rat mannequin, this hydrogel totally degraded inside 21 days, providing a novel technique for scientific prevention of postoperative adhesions. Zhang et al. [112]developed a biodegradable “Janus” zwitterionic hydrogel patch for postoperative anti-peritoneal adhesion by way of uneven design: one facet integrates a self-adhesive poly(acrylic acid-co-N-hydroxysuccinimide acrylate) [P(AA-co-AA-NHS)] brush layer for tissue adhesion, whereas the opposite facet retains zwitterionic poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) (PSBMA) for anti-fouling properties. The adhesive layer achieves steady wet-tissue adhesion by synergistic non-covalent (hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions) and covalent (NHS-amino coupling) interactions, reaching 118.07 J m⁻² interfacial toughness after 24-hour dwell time. The zwitterionic facet resists protein adsorption (3.63% IgG adhesion) and fibroblast attachment (< 10% L929 cell adhesion) by way of hydration barrier results. The hydrogel displays 0.114 MPa tensile energy, 684% elongation at break, and pH-responsive degradation (full hydrolysis in 28 days by way of hyaluronidase). In a rat intestinal abrasion-abdominal wall defect mannequin, SHAN hydrogel achieved 97% adhesion discount (adhesion rating 0.66 at 21 days) in comparison with PBS (4.75) and business HA (2.40), selling collagen deposition (89% wound closure) whereas avoiding secondary irritation. This dual-functional design addresses challenges of conventional anti-adhesion supplies by integrating tissue adhesion, anti-fouling, and biodegradability, providing a promising resolution for stomach surgical procedure.
Uterine adhesions are a typical postoperative downside and might trigger critical problems. Supplies comparable to hydrogels and movies endure from poor dealing with, lengthy gelling occasions, brief residence occasions, and acidic degradation merchandise [113, 114]. Fibrin deposition and fibroblast infiltration scale back the power of supplies to forestall adhesion [115]. Lv et al. [116] ready oxidized hyaluronic Acid/methacryloylated gelatin@polycaprolactone (OD/GM@PG) bioadhesives with a moist adhesive internal layer and an anti-adhesive outer layer. These bioadhesives possessed excessive moist adhesive energy and interfacial toughness, downregulated the expression of inflammatory response-related proteins (S100A8, S100A9) (mRNA diminished by 50%) and inhibited NOD-like Receptor Pyrin Area-Containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation (caspase-1 exercise diminished by 60%) to cut back inflammatory exudation and forestall adhesions. Mao et al. [117] achieved a novel micro/nanopore construction and acid neutralization (The pH worth rises from 4.5 to six.8) by Janus nanofibrous limitations (GelMA-PLA/PGA/Lec). The micro/nanopore construction (The pore diameter measures 200 nm) supplied wonderful permeability and applicable moisture content material, which is crucial to keep up barrier perform and scale back adhesions. As well as, the micro/nanopore construction diminished the danger of adhesion formation by decreasing fibrin deposition (70%) and resisting fibroblast adhesion (Fibroblast adhesion charge decreases to fifteen% (management group: 85%)). The GelMA layer neutralized the acidic surroundings throughout degradation, which helped lower the inflammatory response and mitigate tissue harm, thereby decreasing postoperative adhesions. As well as, Wang et al. [118] ready a Janus microneedle patch utilizing exosomes, which might penetrate the endometrium and firmly adhere to the uterine tissues whereas allowing the continual launch of exosomes. The tissue-adherent and anti-adhesive outer layer construction diminished the formation of tissue fibrosis, was extra biologically steady, simpler to retailer, and extra effectively delivered to focus on tissues [119,120,121]. The patch promoted endometrial angiogenesis and cell proliferation and elevated hormonal response ranges to forestall uterine adhesions, offering a brand new technique to cut back postoperative uterine adhesions and promote tissue therapeutic.
Janus hydrogels have additionally been investigated within the space of postoperative anti-pericardial adhesions. Cardiac surgical procedure might result in postoperative pericardial adhesions because of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses triggered by surgical trauma, resulting in fibrinogen and collagen deposition and macrophage recruitment. Present strategies of stopping pericardial adhesions endure from weak adhesion, incomplete protection, the necessity for sutures that will harm the tissue, and the likelihood that the gel barrier might dissolve too rapidly [122]. Wang et al. [123] reported sustained supply of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-derived Cardiomyocyte Exosomes (iCM-EXOs) by way of injectable Janus hydrogels. These hydrogels exhibited uneven adhesion after photocrosslinking, acted as an antioxidant and anti-pericardial adhesion agent, successfully protected iCM-EXOs from GATA Transcription Issue, and diminished adhesions after cardiac surgical procedure by inhibiting macrophage recruitment from the thorax.
Based mostly on evaluation of the above literature, the anti-adhesion mechanism of Janus hydrogels could be additional interpreted: the non-adhesive floor inhibits tissue adhesion by three pathways: (1) polyethylene glycol (PEG) coatings create steric hindrance to dam protein adsorption; (2) negatively charged surfaces (e.g., sulfonic acid teams) repel negatively charged extracellular matrix parts; (3) clean surfaces scale back mechanical interlocking. Thus, Janus hydrogels present an efficient resolution to cut back postoperative adhesions and have nice scientific potential. Sooner or later, the interactions between Janus hydrogels and the encircling tissue cells have to be studied in depth to know the molecular biology of the anti-adhesion foundation, which might help additional optimization of the design. As well as, we will discover the opportunity of loading anti-adhesion medicine or biologically energetic molecules into Janus hydrogels to boost the anti-adhesion impact or develop a biodegradable Janus hydrogel, which may keep away from the necessity for secondary surgical removing and thus scale back the ache of sufferers.
Loci-saving perform
Janus hydrogels have a variety of purposes in web site preservation and Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) by offering a bodily barrier to guard wounds from exterior contaminants and infections, in addition to sustaining a moist wound surroundings to advertise tissue progress. Shi et al. [124] ready a Janus nanocomposite hydrogel with a barrier perform in opposition to fibroblast invasion, tissue preservation, and restore functionality by utilizing an osmotic cross-linking technique. Its dense, clean high floor has a major barrier perform in opposition to fibroblasts, whereas its free, porous backside floor can help bone regeneration with nanohydroxyapatite. GBR membranes isolate delicate tissues from bone defects, stop the expansion of fibroblasts or epithelial cells with extreme proliferation charges, and improve osteoblast populations to boost bone mineralization and osseous wound occlusion [125]. Nonetheless, present GBR membranes are poor by way of osteogenic impact, antimicrobial properties, in addition to mechanical properties and biodegradability. To beat these limitations, Prajatelistia et al. [126] ready a novel Janus GBR membranes. The chitin nanofiber facet of this membrane promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts. The chitosan layer binds to integrin α2β1 on the floor of osteoblasts by β-1,4 glycosidic bonds (affinity fixed Kd = 0.8 µM). In the meantime, the 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine (MPC) polymer facet successfully inhibits the adhesion of fibroblasts (adhesion quantity < 200 cells/cm²) and restrains the migration of soppy tissues, attaining the impact of integrating the host bone tissue and creating area.This hydrogel may also activate the Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)-2/Smad1 pathway (phosphorylated Smad1 will increase by 3-fold). On the similar time, it up-regulates the expression of Runx2 (mRNA will increase by 2.5-fold) to realize osseointegration. Chen et al. [127] reported the fabrication of Janus fiber/sponge composites utilizing Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs, γ-(:{textual content{F}textual content{e}}_{2}{textual content{O}}_{3})) that shaped an efficient barrier between alveolar bone wounds and gingival delicate tissues, stopping the invasion of epithelial cells and fibroblasts from penetration. The composites exhibited superparamagnetism, which responds to adjustments in an exterior magnetic discipline to realize the modulation of mobile behaviors, comparable to cell recruitment, proliferation, and differentiation, thereby selling tissue restore. As well as, Wang et al. [128] successfully promoted osteoblast precursor cell adhesion, tissue restore, and in vitro angiogenesis by fibroblast-blocking means on the dense facet of the Mg-MgO/PCL Janus-structured composite membrane, in addition to on the porous microfiber facet by the mimetic extracellular matrix and sustained 1(:{textual content{M}textual content{g}}^{2+}) launch. Moreover, the novel bifunctional Janus GBR membrane studied by Ma et al. [129] mixed a Calcium Phosphate-collagen/polyethylene Glycol (CaP@COL/PEG) layer and a Chitosan/poly(acrylic acid) (CHI/PAA) layer with a sandwich construction. This membrane exerted a barrier impact throughout the tissue restore course of, successfully prevented the invasion of non-osteoblasts, supplied favorable situations for the formation of latest bone, and successfully enhanced the impact of tissue restore. The CaP facet releases Ca²⁺ at a focus of 1.2 mM to activate the BMP signaling pathway. The PEG facet inhibits fibroblast migration by steric hindrance (migration charge < 10%). Concurrently, it upregulates alkaline phosphatase exercise (elevated by 2-fold) and promotes the Wnt/β-catenin (Wingless/β-catenin) pathway by downregulating Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1), leading to a 40% improve in β-catenin nuclear translocation, thereby successfully enhancing tissue restore outcomes. Zhou et al. [130] studied Janus Bacterial Cellulose (BC)/MXene membranes utilizing vacuum filtration, etching, and different methods. They discovered that the dense layer performed a key barrier perform throughout tissue restore, successfully prevented the invasion of non-osteoblasts, and supplied a steady area for tissue formation. Within the rabbit calvarial defect mannequin, membrane degradation time was synchronized with new bone formation (12 weeks), and the defect closure charge reached 82%. The morphology of the porous layer of the MXene nanosheets and the membrane supplied a sturdy and steady regenerative area, collectively selling tissue restore.
Janus hydrogels show their distinctive structural and practical benefits in web site preservation and GBR by offering a bodily barrier to guard wounds from exterior contamination and an infection, whereas sustaining a moist wound surroundings to advertise tissue progress. Janus hydrogels present an efficient safeguard for bone tissue restore by the mixture of bodily limitations, antimicrobials, and tissue-engineered scaffolds. Nonetheless, the consequences of Janus hydrogels on cell signaling pathways throughout bone regeneration are nonetheless unclear. A greater understanding of the consequences of Janus hydrogels on osteogenesis-related cell signaling pathways, comparable to Wnt/β-catenin [131], BMP [132], and different pathways, might help optimize their means to advertise bone regeneration. For instance, the consequences of Janus hydrogels on gene expression and protein synthesis of osteoblasts could be analyzed by gene microarray know-how and proteomics strategies to elucidate the molecular mechanism of elevated bone regeneration. Concurrently, by combining floor modification know-how of biomaterials, bioactive molecules able to activating osteoblast signaling pathways could be launched on the floor of Janus hydrogels to boost their osteoinductive properties. As well as, bone defect restore experiments in giant animal fashions might help confirm the effectiveness and security of Janus hydrogels within the preclinical stage, laying the muse for his or her scientific utility.
Stimulus-monitoring perform
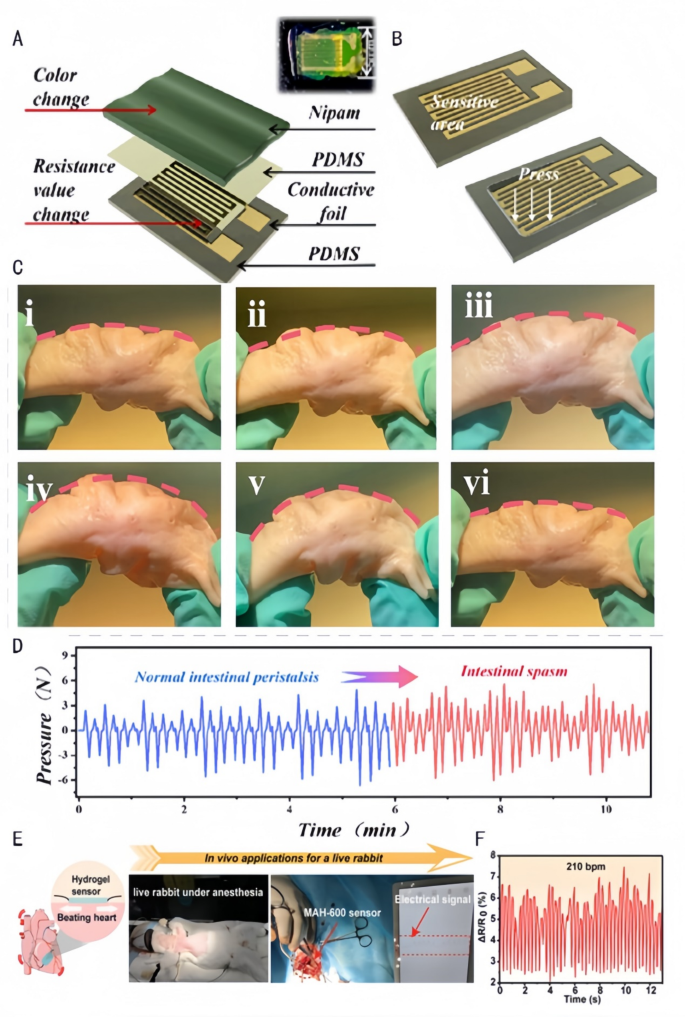
By monitoring key parameters comparable to temperature, humidity, perfusion, and microbial exercise of the wound in actual time, Janus hydrogels present an surroundings that may be exactly managed for wound therapeutic. Chen et al. [133] mixed a hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane substrate and a hydrophilic poly(N-isopropylacrylamido-bis-acrylamidoacrylamide-acrylic acid) (P(NiPAAm-bis-AA)) hydrogel movie to type a medical monitoring instrument that adheres to the intestinal wall. The hydrogel regulates the mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 (mRNA elevated by 3-fold) by way of the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) pathway in response to intestinal peristalsis frequency (detection vary of 0.1–2 Hz). Extra physiological monitoring mechanism of this Janus hydrogel could be additional supplemented as follows: Its ion-sensitive layer allows strain sensing by the next pathways: (1)Temperature-responsive shrinkage/swelling alters resistance; (2)Carboxylic acid teams (-COOH) work together with ions to modulate conductivity; (3)Mechanical deformation transmits alerts by way of microcrack propagation. This instrument stays proof against fouling and self-cleaning, kinds a steady contact between the catheter and the intestinal wall and realizes the transmission {of electrical} alerts by the built-in strain sensor for correct monitoring of intestinal peristalsis and analysis {of electrical} alerts (Fig. 9A.B). Thus, the instrument can be utilized in diagnosing practical intestinal problems, monitoring post-surgical restoration, and evaluating the efficacy of medicine (Fig. 9C.D). Wang et al. [105] ready Janus hydrogels with uneven adhesion properties, robust moist tissue adhesion means, and wonderful mechanical toughness and electrical conductivity by the distribution of free carboxyl teams (-COOH) on each side of the hydrogel on the interface (Fig. 9E), which can be utilized as extremely viscous pressure sensors for monitoring the in vivo heartbeat. The dynamic community is shaped by way of thiol-ene click on response (loss issue tanδ = 0.8), with carboxyl teams electrostatically adsorbing cardiomyocytes (adhesion quantity of 800 cells/cm²). This hydrogel transmits electrical alerts by connexin 43 (Cx43) hole junctions (conduction velocity of 1.5 m/s), detecting coronary heart charge ranges of fifty–250 beats per minute (bpm) with a sensitivity of 0.05 mV/bpm. The analysis of the heartbeat in vivo can be utilized for the well timed evaluation of cardiac well being, prognosis of cardiac arrhythmia, postoperative monitoring (Fig. 9F), and the day by day analysis of train depth and bodily health.
Utility of biomedical sensors in simulating intestinal motility and cardiac exercise. A: Schematic illustration of the constituent layers: a PDMS substrate, a palisade conductive foil (delicate grid), a skinny PDMS layer, and a P(NiPAAm-bis- AA) layer. Inset: an choose [133]. Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. B: Exterior strain causes pressure on the sensor’s delicate unit and consequently adjustments its resistance [133]. Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. C: Simulation of strain adjustments measured by a catheter-based strain transducer within the porcine colon together with intestinal peristalsis. (a) A pressure-sensing catheter was positioned contained in the porcine colon to manage the bending of the colon to simulate intestinal peristalsis. (i) Unique morphology of the porcine colon; (ii) porcine colon bending by 10°; (iii) porcine colon bending by 20°; (iv) (iii) porcine colon bending by 20 [133]; (iv) porcine colon bending by 30°; (v) porcine colon bending by 40°; (vi) porcine colon returning to its preliminary morphology [133]. Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. D: Picture of the peristaltic strain over time for intestinal peristalsis [133]. Copyright 2024, American Chemical Society. E&F: Normalized electrical sign of the beating rabbit coronary heart over time detected by the MAH-600 pressure sensor [105]. Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH GmbH
Janus hydrogels present nice potential within the monitoring of human intestinal motility and cardiac physiology. By combining hydrophobic and hydrophilic materials traits, they obtain protected adhesion to the intestinal wall and preserve stain resistance and self-cleaning properties, offering a steady and intuitive resolution for intestinal monitoring. This uneven adhesion property mixed with wonderful mechanical and electrical conductivity can be utilized as a pressure sensor to precisely monitor physiological actions such because the heartbeat, offering a brand new technological means for human well being monitoring and illness prevention. On the similar time, Janus hydrogels present real-time suggestions on the adjustments within the inner surroundings of the organism by monitoring the physiological alerts throughout the tissue therapeutic course of, evaluating the consequences of tissue restore and regeneration, adjusting the remedy plan in time, and optimizing the restore technique. Nonetheless, there may be nonetheless room for enchancment within the sensitivity and accuracy of Janus hydrogels. Sooner or later, their monitoring efficiency could be improved by materials innovation and sensor know-how optimization, comparable to introducing nanomaterials to boost the responsiveness or accuracy of the sensor. As well as, Janus hydrogel sensors could be developed for multi-parameter monitoring, concurrently monitoring tissue temperature, humidity, pH, inflammatory components, and different indicators, thus offering richer information for a complete understanding of the therapeutic course of. Janus hydrogel sensors will also be mixed with wi-fi transmission know-how to realize distant real-time monitoring, which is handy for healthcare professionals to maintain abreast of adjustments within the affected person’s situation and enhance the effectivity of medical care.
Precision transport
Though endoscopic surgical procedure has been extensively used for minimally invasive procedures, using hydrogel membranes throughout minimally invasive procedures is proscribed by the issue in spreading them to utterly cowl irregular or folded tissue surfaces [134]. Standard hydrogels might break or self-adhere endoscopically throughout minimally invasive procedures. In distinction, because of their construction, Janus hydrogels could be delivered stably by the endoscope. Furthermore, the totally different wettability, pore construction, and chemical composition of the 2 sides of Janus hydrogels enable for the focused loading and managed launch of medicine. This good responsiveness permits the Janus hydrogel to modulate the drug launch charge in response to the adjustments within the surrounding surroundings (e.g., pH, temperature, or ion focus), enabling exact supply [7]. In the meantime, the nice mechanical energy and adaptability of Janus hydrogels ensures the soundness and match of the supply system in advanced organic environments.
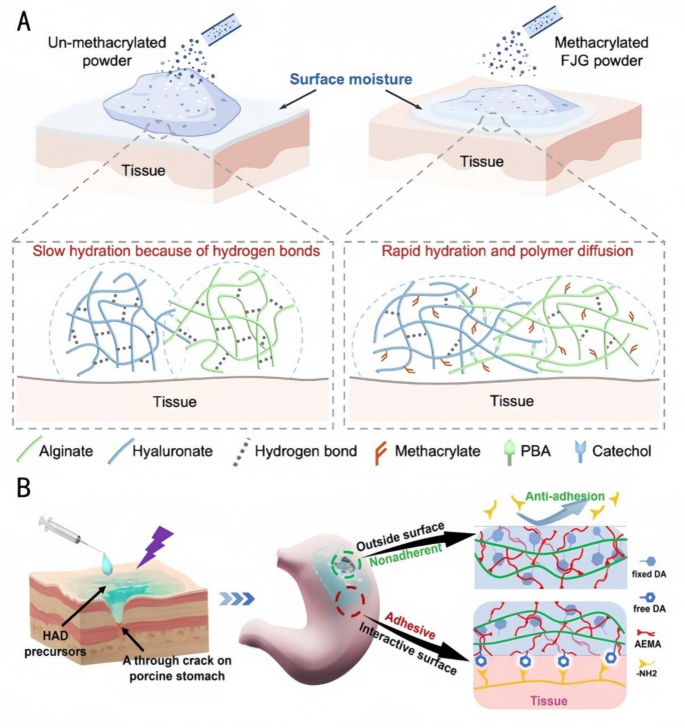
Investigating using Janus hydrogels in endoscopic surgical procedure, Jia et al. [135] ready Quick Gelation (FJG) powders with fast water absorption and quick gelation capabilities (Fig. 10A). They modified the polysaccharide macromolecules by methacrylation to enhance their water absorption means and by utilizing the fast dynamic addition of borate bonds for quick gelation after hydration. The principle parts had been the polysaccharide macromolecules modified by methacrylamide macromolecules, and the higher powder was cationized by remedy with a cationic chitosan resolution to acquire a non-adhesive Janus hydrogel on the higher floor. The Janus hydrogel shaped by FJG powder displays favorable viscoelasticity and an applicable in vivo degradation charge. It may be delivered by a 2.8 mm biopsy channel, protecting 100% of the gastric perforation space (5 mm in diameter). This hydrogel successfully prevents postoperative adhesions whereas additionally that includes simple storage and low-cost supply. Wu et al. [136] fabricated an injectable Janus hydrogel with injectable uneven adherent hydrogels (HADs) by way of a photocuring method and a Minimally Invasive Supply (MID) system [137]. This hydrogel enabled exact supply and fast prevention of fluid leakage in laparoscopic surgical procedure by the sealing and wound-healing capabilities of the hydrogel on the within (Fig. 10B), the anti-adhesive properties of the surface, and using particular syringes for MID and exact injection. It overcomes the issue of most hydrogels being preformed in patch type, missing the power to gelate in situ, and having restricted utility in minimally invasive surgical procedure for gastric perforation. Based mostly on the systematic abstract of the above literature, the exact drug supply mechanism of Janus hydrogels could be deduced as follows: Their uneven construction allows focused launch by way of three pathways: (1) The hydrophilic layer adsorbs medicine and triggers pH-responsive launch; (2) The hydrophobic layer drives unidirectional drug transport utilizing capillary motion; (3) Photothermal-responsive supplies (e.g., PDA) speed up drug launch underneath near-infrared irradiation. These synergistic results thereby obtain exact drug supply.
Functions of FJG powder and HAD hydrogels in tissue engineering. A: Schematic diagram of hydration of FJG powder [135]. Copyright 2023, PNAS. B: Schematic diagram of the Janus HAD hydrogel for sturdy and environment friendly sealing of abdomen tissues: The inner-side floor of HAD hydrogels might type sturdy adhesion on the abdomen floor because of a Michael-type response, whereas the outward-side face of HAD was nonadherent because of the restriction of free DA teams after the Michael-type response post-photocrosslinking [136]. Copyright 2023, Theranostics
Membrane hydrogels are tough to adapt to irregular tissue surfaces, and stability points throughout surgical procedure are tough to resolve [114]. Janus hydrogels not solely present an answer for good tissue compliance, simple storage, and low-cost supply in endoscopic surgical procedure, but in addition allow exact supply and fast fluid sealing throughout surgical procedure by light-curing know-how and MID units. These improved approaches not solely enhance the therapeutic efficacy of the process, but in addition open up new potentialities for Janus hydrogels for use in scientific procedures in minimally invasive surgical procedures, thereby enhancing the affected person’s surgical expertise and restoration course of. Nonetheless, there are nonetheless some urgent points that should be addressed within the sensible utility of Janus hydrogels. At present, little is thought about how Janus hydrogels could be exactly formed on the desired web site and obtain efficient drug launch within the advanced in vivo surroundings. Most research are restricted to in vitro experiments or easy animal fashions and lack in-depth investigation within the human physiological surroundings, making it tough to precisely assess the precise results of Janus hydrogels on totally different people and sophisticated ailments. When focusing on irregular tissue surfaces, it’s tough to make sure the match of hydrogels, which can lead to some tissues not being successfully handled, affecting the general efficacy [116]. Furthermore, as a result of the synergistic relationship between the hydrogel molding course of and drug launch is unclear, exact supply of Janus hydrogels is difficult. In view of those challenges, sooner or later, imaging applied sciences, comparable to magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, mixed with in vivo tracer know-how, can be utilized to watch the supply course of, the molding location, and the dynamics of drug launch from Janus hydrogels in vivo in actual time. This can assist acquire insights into the mechanism of their conduct in advanced physiological environments and supply a foundation for the optimization of their design. By way of materials modification and structural optimization, Janus hydrogels could be designed with self-adaptive means in order that they’ll mechanically alter their morphology in response to the form and traits of the tissue floor and enhance the match on irregular tissue surfaces and the uniformity of drug launch.
Different
The flexibility of Janus hydrogels permits for extra than simply the above talked about biomedical purposes. For instance, Janus hydrogels are additionally extensively used within the anti-infection of the nasal mucosa. The nasal cavity is very vulnerable to postoperative infections and recurrent irritation because of spatial and environmental constraints. Generally used postoperative dilatation sponges can solely isolate the wound however not battle an infection or speed up wound restoration. To advertise fast therapeutic of the nasal cavity, Luo et al. [17] ready a multifunctional amphiphilic wound dressing nanofibrous materials with Janus superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic functionality by utilizing PCL-gelatin fibers as a pump-absorbent layer. The superhydrophilic pump-absorbent layer maintains the moist surroundings of the wound by absorbing and isolating the wound exudate, and in the meantime, the RGD sequence promotes integrin αvβ3 binding (Kd = 1.2 µM), prompts the Focal Adhesion Kinase/Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (FAK/PI3K) pathway (phosphorylation ranges elevated by 3-fold), reduces IL-8 secretion (focus decreased from 200 pg/mL to 50 pg/mL), and upregulates IL-10 expression (elevated by 2-fold), thereby successfully blocking bacterial invasion. The superhydrophobic layer prevents bacterial adhesion and colonization, thus successfully stopping an infection. Lei et al. [138] ready triple-toluene-hardened (MTS)-based Janus hydrogels (MTS@P/DLT) with uneven adhesion (MTS@P/DLT) by using versatile wooden because the skeleton and PVA because the outer matrix. One facet has The viscosity of the decrease double-layer thiol-enclosed click on chemical movie (Twin-Layer Thiol-ene Click on Chemistry Movie, DLT), which is essential for the pliability and anti-adhesion properties of the hydrogel, whereas the opposite facet has the next viscosity. In contrast with atypical hydrogels, Janus hydrogels have bacteriostatic properties and their elevated flexibility in response to the fixed motion of the nasal mucosa enhances the diploma of adhesion to the tissues, creates a sterile and invasive surroundings, and reduces the danger of recurrence of rhinitis.
Janus hydrogel drug transport capability has purposes in anticancer. Lee et al. [139] constructed Janus polysaccharide membranes composed of Chitosan-catechol (Chi-C), which is a powerful adherent, and alginate (Alg), which is an anti-adherent. The formation of a steady bilayer construction with electrostatic interactions allows the management of variations within the energy of tissue adhesion, with the robust adhesion of the Chi-C layer making certain tight binding of the movie to the tissue, and the weak adhesion of the Alg layer offering the mandatory anti-adhesive properties. This Janus membrane can encapsulate the anticancer drug doxorubicin (DOX). The Alg layer releases DOX in an acidic tumor microenvironment (pH 6.0) with a launch charge of 90%, whereas solely < 15% is launched in a impartial surroundings (pH 7.4). DOX inhibits Topoisomerase II exercise (enzyme exercise diminished by 80%) by intercalating into DNA base pairs (Kd = 0.1 µM) and prompts caspase-3/7 (exercise elevated by 4-fold), inducing tumor cell apoptosis (apoptosis charge of 75%). In the meantime, launched DOX promotes dendritic cell (DC) expression of CD80/CD86 (elevated by 3-fold), activating CD8 + T cell responses. Mannose residues within the Alg layer promote M1 macrophage polarization by way of MR receptors (CD86 + cells elevated by 60%). This materials has a DOX loading capability of 8% (w/w), an encapsulation effectivity of 92%, accumulates drug concentrations on the tumor web site 8-fold larger than in regular tissues, achieves a 89.7% tumor quantity inhibition charge over 21 days, and displays no important systemic toxicity, offering an environment friendly and protected resolution for tumor-targeted remedy. Moreover, thiolated chitosan-lithocholic acid nanomicelles for ergotamine supply [140] spotlight a novel technique for enhancing mucosal adhesion and pH-triggered drug launch. This technique demonstrated 89.7% tumor discount in murine fashions by dual-functional mechanisms: thiolation-enhanced mucoadhesion and acid-responsive drug launch at ~ pH 5.5 (near that of tumors. Such improvements might encourage Janus hydrogel designs with uneven layers—one optimized for focused drug supply by way of pH-responsive nanocarriers, and the opposite engineered for antimicrobial or anti-adhesive properties—to reduce systemic toxicity whereas maximizing native therapeutic outcomes.
The design and utility of those modern supplies haven’t solely improved therapeutic efficacy but in addition diminished the danger of postoperative problems and improved the standard of lifetime of sufferers. Nonetheless, the bodily and chemical properties of Janus hydrogels have to be additional optimized to realize a focusing on impact on particular cells or tissues, enhance therapeutic impact, scale back harm to regular cells, and promote tissue restore. For instance, the impact of Janus hydrogels on nasal mucosa cells could be noticed in the long run, along with figuring out whether or not their degradation merchandise within the nasal surroundings will trigger allergy or different opposed reactions. When used for anticancer purposes, it’s crucial to check the distribution and metabolism of Janus hydrogels in tumor tissues to evaluate their toxicity and potential unwanted effects on regular tissues. As well as, the potential of Janus hydrogels within the remedy of different ailments, comparable to ophthalmic ailments and neurological ailments, could be additional explored to supply extra therapeutic choices for the biomedical discipline.