On this examine, we performed an intensive morphological investigation of an E. coli system for the biosynthesis of CdS nanoparticles. Notably, that is the primary report highlighting the connection between minicell formation and nanoparticle biosynthesis in E. coli with out genetic modifications that promote this phenotype.
The formation of minicells, usually attributed to Min system deletion, was initially thought-about devoid of a physiological function. Nevertheless, analysis by Rang et al. (2018) revealed that an E. coli ΔminC pressure exhibited elevated tolerance to streptomycin, with minicells enjoying a job within the disposal of inclusion our bodies and misfolded proteins generated by antibiotic publicity [31]. Equally, a earlier examine from our analysis group demonstrated that, in Min-deletion mutants of E. coli conducting intracellular biosynthesis of CdS QDs, nanoparticles have been sequestered and expelled from the cells contained in the produced minicells, contributing to the upkeep of mobile integrity [33]. These findings point out a detoxifying mechanism for broken parts in E. coli cells related to minicell manufacturing, a course of that seems to be prolonged to nanoparticle biosynthesis, which additionally implies that minicells function automobile for steel disposal from the cell as a detoxifiyng mechanism. Whereas no experiences hyperlink heavy steel publicity to minicell formation in E. coli, earlier research on the consequences of cadmium ions on E. coli cells may present insights. As an example, cadmium ions exert their major results on E. coli cells by way of inducing misfolded protein stress. This stress is mediated by cadmium’s affinity to sulfide current in cysteine and iron-sulfur facilities, forming complexes by binding to thiol teams and changing different transition-metal cations in such sulfur-rich compounds [46,47,48]. Consequently, that is related to a adverse influence on cell division. Particularly, publicity of E. coli cells to cadmium ions and CdS nanoparticles results in cell filamentation and hinders the right formation of the division septum. This inhibition is attributed to a lower within the expression of key division proteins, FtsZ and FtsQ [49, 50]. These findings counsel that cadmium publicity may induce adjustments within the expression of cell division proteins, doubtlessly leading to a minicell-forming phenotype.
The exploration of cell morphology throughout the biosynthesis of steel nanoparticles has been restricted, doubtless because of the dynamic nature of the method and the predominant concentrate on biotechnological functions for organic synthesis evaluation. Within the examine by Marusak et al. (2016) [51], it was famous that the addition of CdCl2 and cysteine as a sulfur supply at varied development phases of E. coli can affect crystal dimension and the localization of cadmium precipitation, enabling extracellular biosynthesis. Equally, a number of research have documented the extracellular biosynthesis of cadmium nanoparticles by way of risky compounds [13, 20, 52], streamlining their preparation, purification, and enhancing the ultimate yield. The relevance of extracellular biosynthesis has supported the examine of the biosynthesis course of as technique of avoiding the poisonous impact of cadmium on bacterial cells. As an example, it was demonstrated that in sea-derived bacterial strains, selling the extracellular biosynthesis of CdS nanoparticles by way of cysteine supplementation alleviates the toxicity of the steel, and the cell doesn’t want to reply by expressing steel efflux proteins or Reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging enzymes [2, 53, 54]. Simillarly, for Shewanella oneidensis, addition of exogenous extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) promotes CdS biosynthesis and enhances cell viability [55]. This behaviour isn’t restricted to cadmium, as steel tolerance and detoxing has additionally been associated to biosynthesis of nanoparticles fabricated from iron [56], copper [57] and terbium [58], simply to call just a few. Nevertheless, the identical has not been totally investigated in intracellular biosynthesis, so understanding the mobile constructions concerned within the disposal of nanoparticles may improve our view of biosynthesis as a resistance mechanism.
In our earlier work, we highlighted that on this system, fluorescence emission turns into concentrated in well-defined polar constructions, both inside the cell or immediately related to the cell poles. This remark was corroborated on this examine by analyzing the fluorescence profiles of cells (Fig. 1D). Apparently, this phenomenon of nanoparticle localization and membrane interplay isn’t distinctive to our system however has additionally been noticed in different biosynthesis setups. For instance, in a pressure expressing a CdS binding peptide, TEM evaluation revealed that nanostructures are related to the cell membrane and poles [59]. Comparable conduct was famous by Marusak et al. (2016) [51], the place CdS nanoparticles synthesized by an E. coli pressure expressing a heterologous cysteine desulfhydrase gene have been primarily situated close to the cell membranes. Moreover, in an E. coli system designed for the biosynthesis of cadmium and selenium QDs, nanoparticles have been predominantly located on the cell poles [60]. A comparable polar localization of nanoparticles was noticed in an E. coli system expressing cystathionine γ-lyase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia for CdS QD biosynthesis [61]. Notably, this noticed phenotype can also be current in different Gram-negative micro organism, resembling species from the Pseudomonas and Psychrobacter genera. In these micro organism, throughout the synthesis of CdS QDs, nanomaterials accumulate close to the cell poles, accompanied by morphological adjustments, resembling lack of membrane integrity [19] or widening of the periplasmic house [62]. This proof helps the speculation that the method of cell division could also be intertwined with QD biosynthesis. These observations led us to hypothesize that QD biosynthesis in micro organism is linked to cell fragmentation and even the era of minicells. This fragments would in flip, remove dangerous cadmium ions from the intracelullar house.
Fluorescence microscopy evaluation revealed varied morphological adjustments and patterns of fluorescence emission in cells following QD biosynthesis (Fig. 2). Particularly, three major patterns have been noticed: fluorescence concentrated at one cell pole (Fig. 2A and B), at each poles (Fig. 2 C, 2D), or randomly distributed inside the cells (Fig. 2F and G). These patterns have been current in 27%, 53%, and 20% of the inhabitants, respectively. Moreover, one other conduct was detected, involving the formation of fluorescent spherical cells adjoining to the cell poles (Fig. 2H and I). Though difficult to detect, we can’t rule out the chance that the decision of the microscope might not permit for the clear remark of those constructions separating from rod cells. If our preliminary speculation is right, these spherical constructions might signify minicells shaped as a mechanism for steel disposal, whereas the polar localization of nanoparticles may signify an intermediate stage by which metals are organized for expulsion. The random distribution of fluorescence emission in some cells might point out areas of nanoparticle biosynthesis that precede localization on the poles.
Given the completely different patterns and cell lengths noticed by way of fluorescence microscopy, we hypothesized that CdS QD biosynthesis is perhaps linked to adjustments in cell size. To discover this, we measured cell size from optical microscopy photographs underneath the assorted situations examined (Fig. 1A). Each cadmium publicity and overexpression of the GshA protein resulted in important adjustments in cell size (Fig. 3A). This impact was extra pronounced when cells have been clustered into three subgroups, revealing that every therapy was related to an general discount in cell dimension (Determine S3). Apparently, when analyzing the cell size distribution following biosynthesis situations within the AG1/pCA24NgshA pressure, we recognized a secondary inhabitants of cells roughly 1 μm in size (Fig. 3A), according to the heterogeneous dimension distribution noticed in minicells [42, 43]. This implies that this secondary inhabitants might signify the formation of minicells underneath these situations. Notably, this phenomenon was not noticed within the management pressure AG1/pCA24N uncovered to cadmium, implying that minicell manufacturing relies on CdS QD biosynthesis and helps their function as detoxifying mechanism. This sample was additional confirmed by analyzing the smaller dimension clusters, which clearly indicated the emergence of this secondary inhabitants underneath the desired situations (Fig. 3B).
As beforehand famous, cadmium publicity in E. coli has been related to a rise in cell dimension [49], fairly than a lower. This discrepancy could possibly be because of the markedly completely different situations utilized in our examine. As an example, cells weren’t repeatedly grown within the presence of cadmium however have been as a substitute grown to the stationary section earlier than being uncovered to the steel for an prolonged interval. Moreover, the cadmium focus utilized in our examine was comparatively low in comparison with different experiences. Our findings may signify a type of “equilibrium” between E. coli biomass and cadmium ions and/or nanoparticles.
Moreover, overexpression of the GshA protein was additionally related to a lower in cell dimension. A examine by Basan et al. (2015) demonstrated that overexpression of a “ineffective” protein (LacZ) led to a rise in cell size and quantity throughout the exponential development section. Nevertheless, the identical examine confirmed that nutrient limitation had the other impact [63]. If our “equilibrium” mannequin is right, we may speculate that the discount in cell dimension related to GshA overexpression could also be because of the nutrient-depleted state of cells following protein overexpression. Moreover, it is very important observe that the redox exercise of the GshA protein is concerned in quite a few mobile processes in E. coli and different organisms [64, 65], so its overexpression may affect cell dimension by way of these processes as effectively.
At present, there are not any experiences documenting minicell formation as a consequence of heavy steel publicity or nanoparticle biosynthesis. Nevertheless, some research have investigated gene regulation associated to cell division and the expression of proteins within the Min system. For instance, in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, the minC gene is downregulated within the presence of iron by way of the Fur protein [66]. Equally, in Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the expression of the minD gene is regulated by the OxyR protein, and cells poor in OxyR exhibit an elevated price of aberrant, non-midline formation of the division septum in comparison with wild-type cells [67], a sample that aligns with our findings (Fig. 3). These precedents counsel that steel publicity in micro organism may induce morphological adjustments, doubtlessly explaining the formation of minicell-like constructions in our system. Moreover, in our system, it is very important contemplate the chance that the nutrient-depleted state could possibly be influencing the mobile response to cadmium publicity, thereby selling minicell formation. Nevertheless, additional analysis is required to discover this risk.
TEM evaluation revealed well-defined electron-dense materials in cells from the pressure AG1/pCA24NgshA after biosynthesis situations (Fig. 4E, 4 F). As a result of overexpression of the GshA protein on this pressure, these constructions are doubtless inclusion our bodies. That is substantiated by the upper proportion of cells with any such electron-dense materials in pressure AG1/pCA24NgshA in comparison with the management pressure, and the elevated proportion after publicity to the steel precursor CdCl2 (Fig. 4G). This implies that steel publicity is augmenting the variety of inclusion our bodies, a phenomenon already documented within the literature [46,47,48]. Moreover, this was corroborated by way of SDS-PAGE evaluation, revealing the presence of a part of the GshA protein within the insoluble fraction of proteins in pressure AG1/pCA24NgshA after IPTG induction (Fig. 5).
Minicell formation was confirmed by way of TEM (Fig. 7). Moreover, minicells in formation have been discovered to be loaded with electron-dense inclusion our bodies and nanometric materials (Fig. 7B and D), offering assist for the speculation of their function within the disposal of cadmium steel as nanoparticles from the cell. A earlier report by Rang et al. (2018) [31] elucidated the function of minicell formation in eliminating misfolded proteins and inclusion our bodies from cells. On this mannequin, inclusion our bodies relocate to cell poles for encapsulation in minicells, subsequently resulting in their expulsion. An identical course of could possibly be occurring in our system, the place after the relocation of nanoparticles certain to inclusion our bodies to poles, they’d be encapsulated in minicells for detoxing from the cell.
In pressure AG1/pCA24NgshA, electron-dense materials localization exhibited comparable patterns to these visualized by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 2), primarily characterised by the polar localization of electron-dense materials (Fig. 6A and B). This implies that biosynthesized nanoparticles are doubtless certain to the inclusion our bodies generated within the course of. Earlier characterization of those nanoparticles revealed that they have been GSH-capped [14]. Moreover, to regulate the intracellular quantity of GSH, the GshA enzyme is regulated by GSH, which acts as a aggressive inhibitor by binding to GshA’s cysteine-binding website [68, 69]. Therefore, it’s believable that QDs binding to extra GSH, generated by the overexpression of GshA, are additionally binding to the GshA protein forming inclusion our bodies. A number of experiences on bacterial QD synthesis counsel that these nanoparticles exhibit a capping fabricated from natural matter, proteins, and different biomolecules, enjoying a job in nanoparticle formation, stabilization, and general properties [13, 14, 70, 71]. Subsequently, the interplay between inclusion our bodies and nanoparticles throughout the biosynthesis course of is believable. Furthermore, research have reported the preferential polar localization of assorted proteins, together with chaperones resembling IbpA [31] and GroEL [72]. Chaperones have been proposed to play a job within the synthesis of nanoparticles [70], and their means to relocate inside the cell may contribute to the polar accumulation of inclusion our bodies and nanoparticles. Moreover, new protein components in E. coli have been described for the polar localization of proteins, resembling TmaR, a protein concerned within the polar localization of elements of the phosphotransferase system [73]. Moreover, different proteins have been reported to “mark” spots for division websites that ultimately flip into poles, as demonstrated by chemotaxis receptors in E. coli, which kind clusters in division websites two generations earlier than precise division [74].
One other remark made by way of TEM was the segregation of inclusion our bodies to daughter cells following cell division (Fig. 6C and D), which may clarify the buildup of electron-dense materials in a single cell pole (Fig. 6E, 6 F). This phenomenon aligns with the cell ageing mannequin proposed by Shi et al. (2020), whereby older poles accumulate broken parts. After cell division, one daughter cell, known as the “outdated daughter”, inherits these parts and displays slower development, preserving the health of the “new” daughter [45]. In our system, the same situation might happen, the place misfolded proteins and steel nanoparticles synthesized throughout biosynthesis are relocated to the cell poles. Upon division, these elements could be retained within the outdated daughter cell, facilitating the manufacturing of metal-free cells. This mechanism suggests a possible technique by which cells rid themselves of broken or dangerous elements, thereby making certain the vitality of newly shaped cells. Apparently, we noticed minicell formation solely in cells with electron-dense materials gathered at a single pole (Fig. 7), however not in these with accumulation at each poles. This may point out that for minicell formation to happen, the cell have to be in a good state. A division step leading to single-pole accumulation could possibly be a prerequisite for selling minicell formation, although additional analysis is required to verify this speculation.
Our outcomes immediate the query of how minicells are generated in some cells in response to QDs biosynthesis. The low proportion of cells producing minicells underneath CdS nanoparticles biosynthesis situations (Fig. 3) means that this isn’t a physiologically promoted mechanism, particularly contemplating the obvious want for GshA overexpression for its incidence. Within the examine by Hoffman and Frank (1963) [75], publicity of assorted E. coli cultures to elevated temperature (43.5 °C) resulted in just one minicell out of “a number of thousand” cells. This underscores the problem of finding out this phenomenon in cells missing mutations within the Min system. Concerning the molecular mechanism for minicell formation, it could possibly be mediated by a common down-regulation of genes concerned in cell division as a consequence of cadmium publicity [76]. As talked about earlier, publicity of E. coli cells to cadmium ions and CdS nanoparticles induces cell filamentation and inhibits the proper formation of the division septum, involving a lower within the expression of FtsZ and FtsQ division proteins [49, 50]. These proteins play a job within the formation of the “Z-ring” within the middle of the cell [77]. Moreover, the Min system finely regulates cell division location, and E. coli cells poor in it exhibit excessive filamentation and divide in random spots, resulting in the formation of minicells [30]. Moreover, down-regulation of different elements of the E. coli divisome may additionally contribute to this phenomenon. Unpublished outcomes from our group point out a lower within the expression of the ZapB protein underneath CdS QDs biosynthesis, and the deletion of this protein, together with decrease expression of FtsZ, induces the minicell formation phenotype [78], offering one other potential clarification for this incidence.
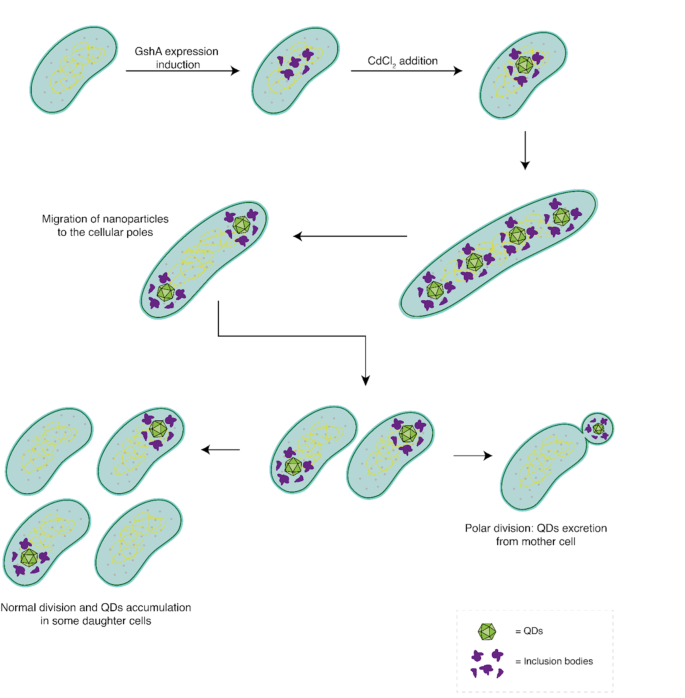
Our outcomes, mixed with earlier characterizations of the system [14, 33], allow us to suggest a mannequin illustrating the assorted morphological adjustments that happen in pressure AG1/pCA24NgshA following the biosynthesis of CdS nanoparticles (Fig. 8). The method begins with the induction of GshA protein expression by IPTG, resulting in a rise in intracellular GSH focus and the formation of inclusion our bodies. Subsequently, the addition of the steel precursor to the tradition media initiates nanoparticle biosynthesis all through the cytosol. These nanoparticles bind to the inclusion our bodies, both by way of the GSH cap or by way of interactions with chaperone proteins. The synthesized nanoparticles are then relocated to each cell poles as an intermediate mobile kind. Following this, the cell resumes regular division, permitting for the segregation of QDs into daughter cells. At this level, two potentialities come up: (1) By successive cell divisions, QD-free cells are generated, which might proliferate usually. (2) If a cell experiences down-regulation of things concerned in septum localization, polar division might happen, ensuing within the formation of a minicell that encapsulates and disposes of the steel from the cell.
Morphologic mannequin of cadmium nanoparticles biosynthesis in E. coli AG1/pCA24N gshA. First, the GshA protein is overexpressed within the AG1/pCA24NgshA pressure, selling the formation of inclusion our bodies. Subsequently, steel precursors are included into the cell, the place nanoparticles are synthesized by the motion of intracellular GSH. These nanoparticles, related to inclusion our bodies, are then relocated to the cell poles. Following this, cell division happens, leading to cells with a single cell pole containing an accumulation of QDs. Regular division can proceed, resulting in the sequential accumulation of QDs in some cells whereas permitting the formation of cadmium-free cells. Alternatively, polar division might happen, producing a minicell that encapsulates the nanoparticles and separates them from the principle cell