Impressed by the standard bee, robotics researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Expertise (MIT) have designed insect-sized aerial bots with a reimagined wing system that may fly for as much as 1,000 seconds – 100 occasions greater than any related bots we have seen up to now.
These bots, which weigh lower than a gram, function flapping wings that not solely enable for prolonged flights, but additionally elevated agility – sufficient to drag off somersaults and hint infinity symbols within the air. And at a mean velocity of 11.8 inches per second (30 cm/s), they’re faster than fruit flies.
The tiny robots are a giant deal as a result of this might unlock a exact methodology to artificially pollinate vegetation in multilevel warehouses, enabling the cultivation of vegatables and fruits indoors at scale , and decreasing the necessity for huge farmlands.

MIT
They might additionally increase the vital job of pollination normally dealt with by bees, which have been dying by the hundreds of thousands and even billions world wide over the previous few years, as a result of harsh results of pesticides and habitat loss. A current survey carried out this yr noticed greater than 200 business beekeepers within the US report common losses of their bee populations exceeding 50%, with an estimated monetary influence of over US$139 million.
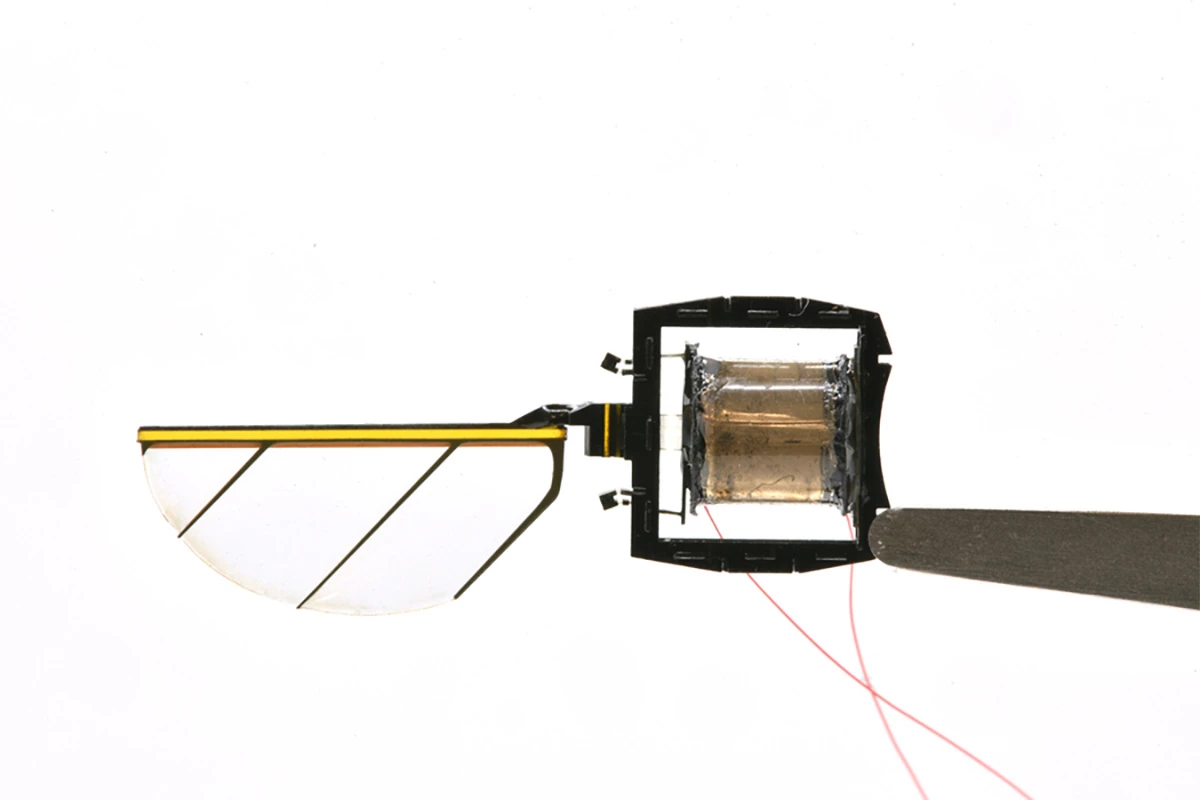
So how do you construct a greater bee-bot? Earlier designs featured eight wings in units of two. Because it seems, the association of those wings precipitated them to blow air into one another after they flapped, decreasing their carry power.
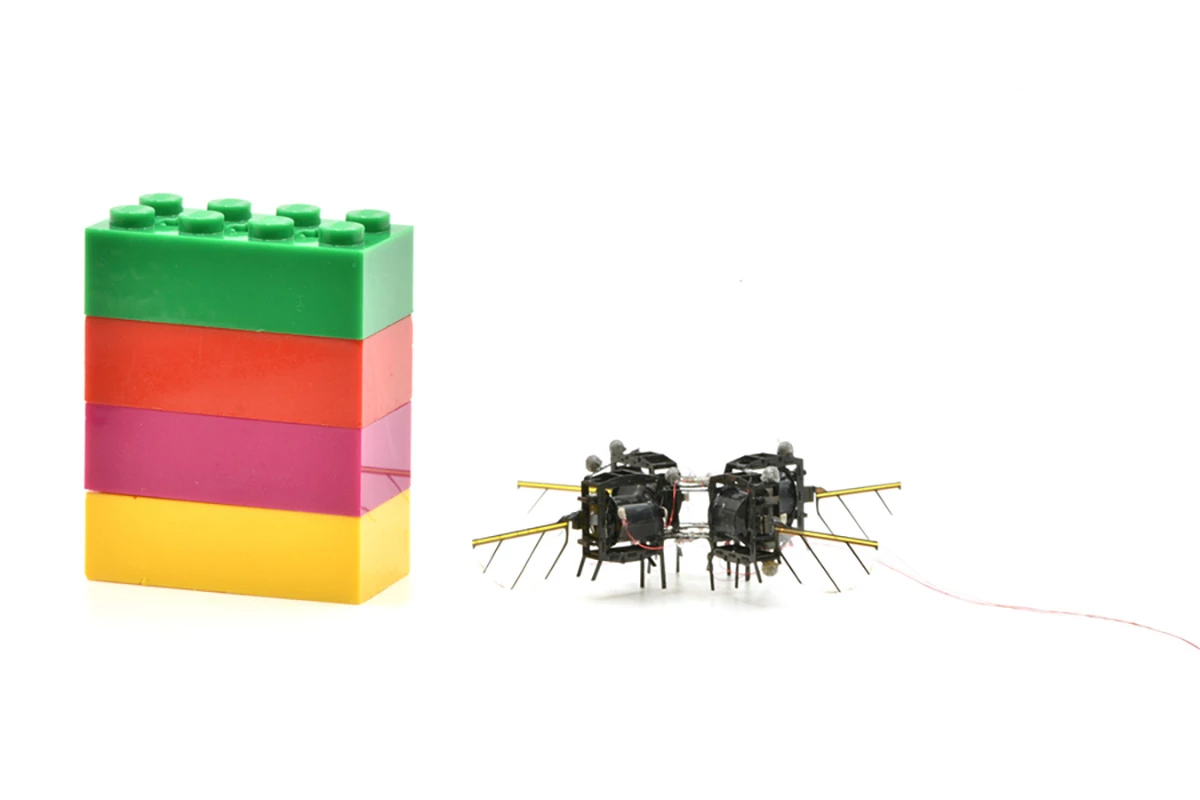
The analysis staff’s up to date method reduces the variety of wings from eight to 4. That not solely stabilizes them and improves their capability to carry the sub-gram bot off the bottom, but additionally makes room for added digital elements.
MIT
These wings use delicate actuators constituted of layers of elastomer sandwiched between skinny carbon nanotube electrodes which might be rolled right into a cylinder – a kind of synthetic muscle. When these muscle tissues quickly compress and elongate, they generate mechanical power that causes the wings to flap.
MIT
The revamped design ensures there’s much less pressure on these synthetic muscle tissues after they transfer at excessive frequencies. There are additionally longer hinges which might be higher at dealing with stress from the flapping wings. Every robotic suits in a 4 cm x 4 cm (1.575 x 1.575 inches) sq..

MIT
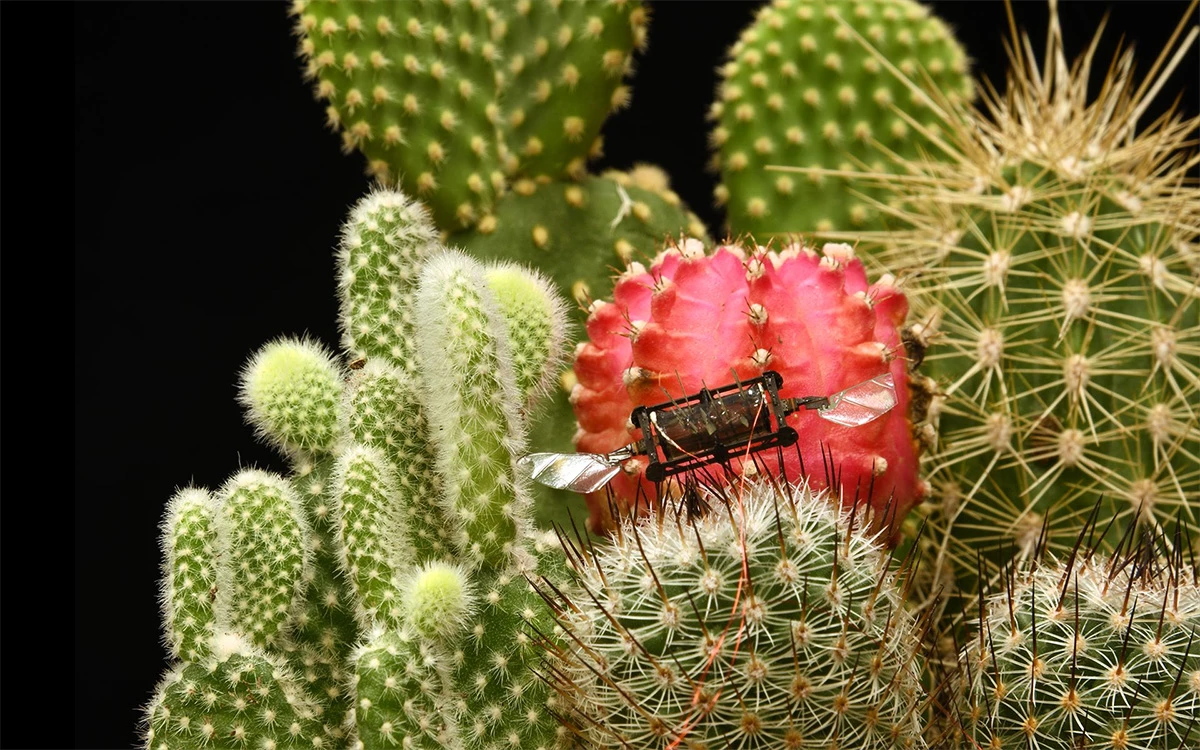
These adjustments enable the microbots to fly for as much as 17 minutes at a time, whereas transferring sooner than any earlier designs and pulling off physique rolls and double flips. Meaning they may effectively cowl predetermined flight paths and make exact maneuvers.

MIT
The researchers imagine there’s room for additional enchancment with these miniscule flying machines: extending flight time to 10,000 seconds utilizing the brand new design, becoming batteries and sensors within the house freed up by decreasing the variety of wings on board, and bettering their precision in flight to allow them to land and take off from the middle of a flower. That might allow a variety of purposes outdoors the lab, together with mechanical pollination in vertical farms.
Supply: MIT Information